

This material is based upon work supported by the National Science Foundation under Grant Number (NSF Grant Number) CNS-1218181. Any opinions, findings, and conclusions or recommendations expressed in this material are those of the author(s) and do not necessarily reflect the views of the National Science Foundation.
Project Summary:
GATE: Greening At The Edges refers to the transformation of the access portion of communications infrastructure into an energy efficient version, i.e., an environmentally friendly version. Thus, the objective of this research is to green both wireline and wireless access networks which currently consume a significant amount of energy of communications infrastructure owing to the large quantity of access nodes. To provision high data rates to meet end users’ increasing bandwidth demands in the future, access networks will upgrade their provisioning capacity and correspondingly experience further increase of energy consumption. To achieve energy efficiency, the PI proposes to evaluate the energy efficiency of various techniques which can increase the capacity of access networks, and introduces a framework of capacity adaptive green access networks to reduce a significant amount of energy consumption by taking advantage of the bursty and dynamic nature of the access network traffic. The proposed research focuses on two specific access networks: optical access networks and wireless cellular access networks. The energy efficiency evaluation provides benchmarks on upgrading current access networks to higher capacity ones in an energy efficient manner. The proposed capacity-adaptive access networks design will provision high capacity networks with reduced energy consumption. The capacity-adaptive access network stays in the “high-capacity high-power” mode when the network is heavily loaded with bandwidth-hungry applications such as video streaming, and switches into the “low-capacity low-power” mode when the network is lightly loaded with less bandwidth demanding applications such as voice and future smart grid traffic.
Research Objective
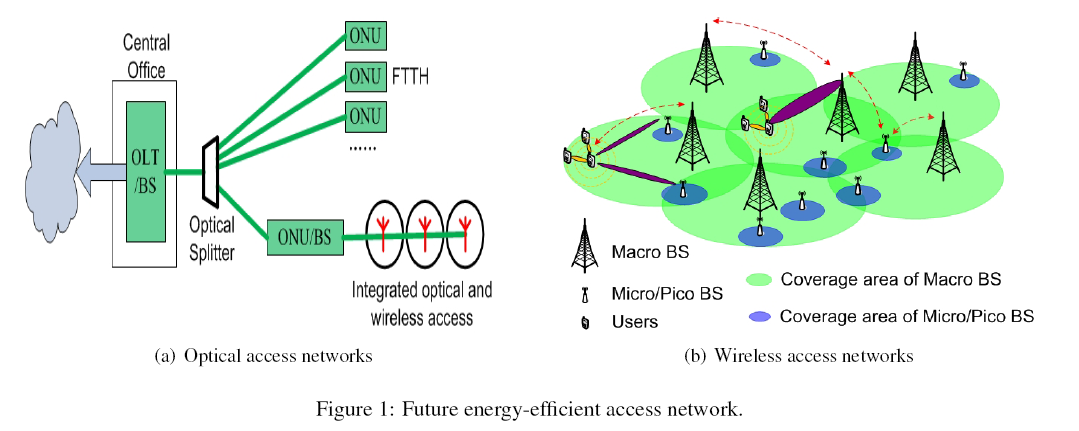
The proposed project, GATE: Greening At The Edges, aims to transform the access portion of communications infrastructure into an energy efficient one. In the future high capacity access networks, the PI envisions that the wireline access part will be made up of fiber-to-the-home or hybrid fiber-to-the-node (FTTN), and the wireless part will be provisioned by various advanced technologies, such as advanced antenna techniques, heterogeneous networks with mixed high/low power base stations deployment, and cooperative communications. Greening such high capacity access networks is a great challenge of the coming decade. To tackle the challenge, the PI introduces the “capacity-adaptive” feature into the envisioned network as shown in Fig. 1. The “capacity-adaptive” feature helps decrease the network energy consumption for the following reasons. While many applications at end users are bandwidth demanding, end users may not run these applications all the time. According to the daily traffic pattern for Swedish and Spanish DSL and FTTH households, the residential access network traffic peaks around 8:00 pm, bottoms between 4:00 am and 6:00 am, and the peak to bottom ratio is as large as 4:1. Thus, a significant amount of energy has been wasted by provisioning the same high data rate to end users all the time. Taking advantage of the bursty and dynamic nature of the access network traffic, the PI proposes a capacity-adaptive green access network which reduces the network energy consumption by switching from the “high-capacity high-power” mode into the “low-capacity low-power” mode when the network is lightly loaded.
Publications:
Tao Han and Nirwan Ansari, “Offloading Mobile Traffic via Green Content Broker”, IEEE Internet of Things Journal, vol.1, no.2, pp.161,170, April 2014.
Tao Han and Nirwan Ansari, “Provisioning Green Energy for Small Cell BSs”, in Proc. Of IEEE GLOBECOM 2014, Austin, Texas, USA.
Tao Han and Nirwan Ansari, “Smart Grid Enabled Mobile Networks: Jointly Optimizing BS Operation and Power Distribution”, in Proc. Of IEEE ICC 2014, Sydney, Australia.
Tao Han and Nirwan Ansari, “Enabling Mobile Traffic Offloading via Energy Spectrum Trading”, IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, vol.13, no.6, pp.3317,3328, June 2014.
Tao Han and Nirwan Ansari, ”On Optimizing Green Energy Utilization for Cellular Networks with Hybrid Energy Supplies,” IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, vol.12, no.8, pp.3872-3882, August 2013.
Tao Han and Nirwan Ansari, “Powering Mobile Networks with Green Energy”, IEEE Wireless Communications Magazine, vol.21, no.1, pp.90,96, February 2014.
Tao Han, Nirwan Ansari, “Auction-based Energy-Spectrum Trading in Green Cognitive Cellular Networks,” Accepted by Proc. 2013 IEEE International Conference on Communications (ICC 2013), Budapest, Hungary.
Tao Han, Nirwan Ansari, “Energy Agile Packet Scheduling to Leverage Green Energy for Next Generation Cellular Networks,” Accepted by Proc. 2013 IEEE International Conference on Communications (ICC 2013), Budapest, Hungary.
Tao Han and Nirwan Ansari, “Optimizing Cell Size for Energy Saving in Cellular Networks with Hybrid Energy Supplies,” IEEE Globecom 2012, Anaheim, CA, USA.
T. Han, J. Zhang, and N. Ansari, “Chapter 17: Green Broadband Access,” Handbook of Green Information and Communication Systems, (M Obaidat, A. Anpalagan, and I. Woungan, ed.), Academic Press, ISDN: 978-0-1241-5844-3, pp. 441-465, 2013.
Jingjing Zhang, Mina Taheri Hosseinabadi, and Nirwan Ansari, "Standards-compliant EPON Sleep Control for Energy Efficiency: Design and Analysis," accepted for publication in IEEE/OSA Journal of Optical Communications and Networks.
N. Ansari and J. Zhang, “Chapter 8: Green Passive Optical Networks,” in Media Access Control and Resource Allocation for Next Generation Passive Optical Networks (authored by Nirwan Ansari and Jingjing Zhang), Springer, ISBN-13: 978-1461439387, 2013.
Patents:
Nirwan Ansari, Tao Han, “Optimizing Cell Size for Energy Saving in Cellular
Networks with Hybrid Energy Supplies,” International Patent Application No.
PCT/US2012/062135, filed on Oct. 2012.
Nirwan Ansari, Tao Han, “Trading Spectrum for Energy Savings in Green
Cognitive Cellular Networks,” International
Patent Application No. PCT/US2013/034848, filed on April. 2013.