

WHAT IS QM?
 QM stands for 'Quality Manufacturability.'
QM stands for 'Quality Manufacturability.'
 In any repetitive production facility, no matter how perfect the operations are, defective products will intermittently appear in the output. Even if a plant targets a 100% quality yeild, then in all probability it will achieve this target only if an extensive effort is expended in monitoring and inspecting the processes. An important question in any analysis of quality problems is, "where do defects or quality problems originate".
In any repetitive production facility, no matter how perfect the operations are, defective products will intermittently appear in the output. Even if a plant targets a 100% quality yeild, then in all probability it will achieve this target only if an extensive effort is expended in monitoring and inspecting the processes. An important question in any analysis of quality problems is, "where do defects or quality problems originate".
 The figure below describes the spectrum of sources for quality problems
The figure below describes the spectrum of sources for quality problems
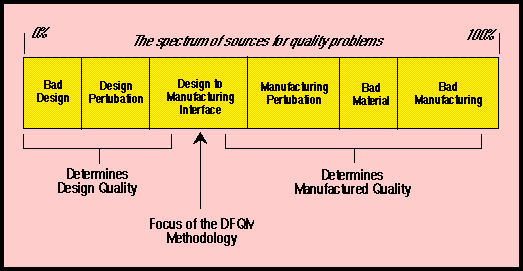
 There are six sources of quality problems in manufactured goods. These are:
There are six sources of quality problems in manufactured goods. These are:
- Bad design refers to prblems in which the design is fundamentally incorrect (e.g, using a heat sensitive adhesive to affix parts that are subjected to high temperatures).
- Design perturbation refers to problems in which the design is inherently sound but certain key parameters need to be further adjusted to improve quality (e.g, changing the elasticity of the rubber molding on a car door).
- Design to manufacturing interface refers to problems in which the design is sound, but from a manufacturing point of view the potential for defects arising exists (e.g, assembling two parts to close tolerances when multiple mating surfaces exist).
- Bad material refers to problems existing in materials procured from outside vendors.
- Manufacturing perturbation refers to problems in which some of the production processes, including inspection and monitoring, need modifications so as to further improve the yeild (e.g, controlling the pressure in an injection molding machine).
- Bad manufacturing refers to problems that stem from a lack of skill, training, discipline, or inadequacy in terms of processing capabilities (e.g, a sheet metal press is operated improperly by an inattentive worker).
 The first two sources determine the design quality of the product. Design quality is defined as the utility of the product as perceived by the customer. Juran and Deming among others, measure this utility in terms of: (i) Functio
nality (ii) Usability (iii) Reliability (iv) Performance (v) Serviceability (vi) Availability, and (vii) Price. It is quite possible that a product which is manufactured according to specifications and with no defects, will still be perceived as having low
quality.
The first two sources determine the design quality of the product. Design quality is defined as the utility of the product as perceived by the customer. Juran and Deming among others, measure this utility in terms of: (i) Functio
nality (ii) Usability (iii) Reliability (iv) Performance (v) Serviceability (vi) Availability, and (vii) Price. It is quite possible that a product which is manufactured according to specifications and with no defects, will still be perceived as having low
quality.
 The last three sources determine the manufactured quality of the product. Manufactured quality is defined as the xetent to which a product deviates from its design specs. Traditionally the focus of quality management efforts has
been on improving the manufactured quality of the products. Typically, these efforts would use incoming inspection to counter bad material, and cause effect analysis and statistical process control to counter manufacturing perturbation or bad manufacturing
.
The last three sources determine the manufactured quality of the product. Manufactured quality is defined as the xetent to which a product deviates from its design specs. Traditionally the focus of quality management efforts has
been on improving the manufactured quality of the products. Typically, these efforts would use incoming inspection to counter bad material, and cause effect analysis and statistical process control to counter manufacturing perturbation or bad manufacturing
.
 The third source determines the quality manufacturability of a product. The QM of a design is defined as an indicator of the likelihood that defects will occur during it's manufacture.
The third source determines the quality manufacturability of a product. The QM of a design is defined as an indicator of the likelihood that defects will occur during it's manufacture.
Maintained by Dr.Das
Sanchoy
 Quick jump to main page!
Quick jump to main page!  Back to The QM Research Project page!!
Back to The QM Research Project page!!


 Home page
Home page  QM Project
QM Project  People
People  Publications
Publications  DFQM Software
DFQM Software  Mail
Mail  QM stands for 'Quality Manufacturability.'
QM stands for 'Quality Manufacturability.' In any repetitive production facility, no matter how perfect the operations are, defective products will intermittently appear in the output. Even if a plant targets a 100% quality yeild, then in all probability it will achieve this target only if an extensive effort is expended in monitoring and inspecting the processes. An important question in any analysis of quality problems is, "where do defects or quality problems originate".
In any repetitive production facility, no matter how perfect the operations are, defective products will intermittently appear in the output. Even if a plant targets a 100% quality yeild, then in all probability it will achieve this target only if an extensive effort is expended in monitoring and inspecting the processes. An important question in any analysis of quality problems is, "where do defects or quality problems originate". The figure below describes the spectrum of sources for quality problems
The figure below describes the spectrum of sources for quality problems
 There are six sources of quality problems in manufactured goods. These are:
There are six sources of quality problems in manufactured goods. These are:  The first two sources determine the design quality of the product. Design quality is defined as the utility of the product as perceived by the customer. Juran and Deming among others, measure this utility in terms of: (i) Functio
nality (ii) Usability (iii) Reliability (iv) Performance (v) Serviceability (vi) Availability, and (vii) Price. It is quite possible that a product which is manufactured according to specifications and with no defects, will still be perceived as having low
quality.
The first two sources determine the design quality of the product. Design quality is defined as the utility of the product as perceived by the customer. Juran and Deming among others, measure this utility in terms of: (i) Functio
nality (ii) Usability (iii) Reliability (iv) Performance (v) Serviceability (vi) Availability, and (vii) Price. It is quite possible that a product which is manufactured according to specifications and with no defects, will still be perceived as having low
quality. The last three sources determine the manufactured quality of the product. Manufactured quality is defined as the xetent to which a product deviates from its design specs. Traditionally the focus of quality management efforts has
been on improving the manufactured quality of the products. Typically, these efforts would use incoming inspection to counter bad material, and cause effect analysis and statistical process control to counter manufacturing perturbation or bad manufacturing
.
The last three sources determine the manufactured quality of the product. Manufactured quality is defined as the xetent to which a product deviates from its design specs. Traditionally the focus of quality management efforts has
been on improving the manufactured quality of the products. Typically, these efforts would use incoming inspection to counter bad material, and cause effect analysis and statistical process control to counter manufacturing perturbation or bad manufacturing
. The third source determines the quality manufacturability of a product. The QM of a design is defined as an indicator of the likelihood that defects will occur during it's manufacture.
The third source determines the quality manufacturability of a product. The QM of a design is defined as an indicator of the likelihood that defects will occur during it's manufacture.
Quick jump to main page!
Back to The QM Research Project page!!