| Physics 321 |
|
Prof. Dale E. Gary
NJIT |
Interstellar Medium
Interstellar Medium (ISM)
Solar wind and IPM (Interplanetary Medium)

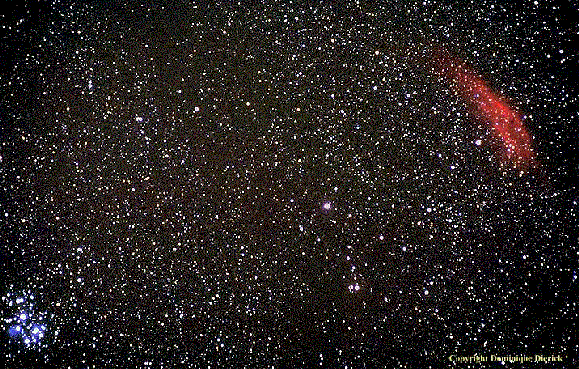
Gas vs. Dust:There are three aspects of the Interstellar Medium in this photograph. The blue nebula at left surrounding the stars of the Pleiades is a reflection nebula, which scatters blue light from the stars. The red nebula at right (California nebula) is an emission nebula, shining in the red light of hydrogen-alpha. In the upper left and slanting diagonally across the middle of the photograph, the background stars appear to be less numerous due to interstellar absorption from dust, which obscures the more distant stars.
Dark Nebulae and Extinction
Extinction (= Absorption + Scattering) means reduction of overall brightness of objects seen through dust. Distance modulus equation is modified when we take dust into account:
Interstellar Reddeningm - M = 5 log d - 5 + A where A is amount of absorption in magnitudes. For A = 1, star is reduced in brightness (flux) by a factor of 2.5. If A were uniform throughout galaxy, then A = kd (proportional to distance) but A is not uniform.
Dust in a galaxy
Nature of Interstellar GrainsWhen you see dust from the side, it appears BLUE and polarized. This polarization does not necessarily depend on grains being elongated.
Pleiades
Again, 99% of ISM by mass is gas, and there are 1012gas "particles" for every dust grain.
Interstellar Absorption
Lines
Supernovae
Image, Latest Image (shock wave slams into ring)
Interstellar Radio
Lines
21-cm lineRecombination lines
- Lowest energy state of hydrogen
- Electron in one of two spin states "up" or "down"
- Define "up" to be parallel with proton spin--then this is higher energy state--would rather be antiparallel
- Energy difference between "up" and "down" corresponds to radio photon of 21 cm wavelength
- Spontaneous flip occurs only once every few million years!
- Collisions in ISM occur once every 400 years, so most flips are due to collisions (no radiation)
- Rare photon emission, but there are enormous numbers of H atoms along each line of sight, so line is strong!
Molecular Lines
- Electrons recombining with hydrogen in H II regions can attach in very high excitation levels, then transition to slightly lower ones, i.e. n = 105 to n = 104. These low-energy transitions give off low-energy photons in the radio region of the spectrum, giving another way to study H II regions.
- CO rotational line, with J = 0 to 1 transition at 115 GHz, and the 1 to 2 transition at 230 GHz. These correspond to mm wavelengths--radio again.
- Molecules that have been detected: CO, CN, OH, H2CO, CH3OH, H2O, NH3, HCN, HC3N, HNCO
- Most molecules, however, are good old H2 (molecular hydrogen).
- Chance of these forming in ISM seem very small (one collision every 400 years) but
- dust helps
- provides place to collect and hold atoms while molecules form over millions (perhaps billions) of years
- shadows fragile molecules from dissociating radiation
- Widespread existence of molecules has implications for extraterrestrial life.
Inside a molecular cloud -- OMC-1: Image
Star formation in M16: link
Egg Nebula: picture