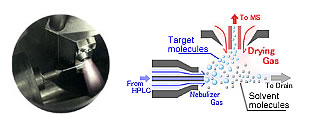
Some methods
for nutrients in water
Ammonia:
The sample is
buffered at a pH of 9.5 with a borate buffer in order to decrease
hydrolysis of cyanates and organic nitrogen
compounds, and is distilled into a
solution of boric acid. Alkaline phenol and hypochlorite react
with ammonia
to form indophenol blue that
is proportional to the ammonia concentration.
The blue color formed is intensified with sodium nitroprusside and measured
colorimetrically.
Nitrate-Nitrite:
A filtered sample is passed through a column containing
granulated copper-cadmium
to reduce nitrate to nitrite. The nitrite (that was originally
present
plus reduced nitrate) is determined by diazotizing with sulfanilamide
and
coupling with N-(1-naphthyl)-ethylenediamine
dihydrochloride to form a
highly colored azo dye which is measured
colorimetrically. Separate, rather
than combined nitrate-nitrite, values are readily obtained
by carrying out the
procedure first with, and then without, the Cu-Cd reduction step.
Phosphorous:
Ammonium molybdate and antimony
potassium tartrate react in an acid
medium with dilute solutions of phosphorus to form an
antimony-phospho-molybdate complex. This complex is reduced to an
intensely blue-colored complex by ascorbic acid. The color is
proportional to
the phosphorus concentration.
Only orthophosphate forms a blue color in this test.
Polyphosphates (and some
organic phosphorus compounds) may be converted to the orthophosphate
form by sulfuric acid hydrolysis. Organic phosphorus compounds
may be
converted to the orthophosphate form by persulfate
digestion
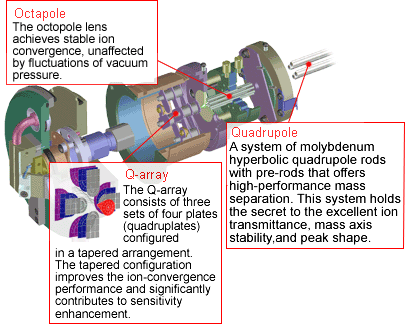
MS-MS Mass separation device