Introductory problem solutions
(Don't peek until you have tried the problems!)
- Cr has atomic number of 24, The major isotope of Mg has atomic mass of 24.
Atomic number indicates number of protons and magnitude of positive charge
on the nucleus. Atomic mass number of an isotope is the total number of protons
and neutrons in the nucleus. Atomic mass of an element is the weighted average
of the atomic mass numbers of all the naturally occurring isotopes, in their
usual abundances.
- An isotope is an atom of an element with a specific number of neutrons in
the nucleus. The number of protons defines the chemical properties and the
elemental identity of an atom, but the number of neutrons can vary, giving
rise to isotopes. An element is composed of atoms of a single atomic number.
A neutron is a nuclear particle with the same mass as a proton, but no charge.
A proton is a nuclear particle with a mass of 1 atomic mass unit, and a charge
of +1. An electron has a mass which is negligible compared to the proton or
neutron, and a charge of -1. Electrons are involved in chemical bonding and
reactions. An ion is a molecule or atom which has more or fewer electrons
than protons, and therefore carries a net positive or negative charge.
- Elemental iodine is reduced by gaining electrons, forming iodide ions,
I-.
- Oxidation of elemental iron, Fe0, forms Fe2O3,
ferric oxide or rust.
- A mole is a collection of 6.02 x 1023 particles, which may be
molecules, atoms, ions etc. A gram mole will weigh, in grams, the same number
as the atomic or molecular weight of the particles. Therefore, a mole of carbon
(atomic weight 12.0 amu) weighs 12 grams.
- Molar mass is the sum of the atomic masses. For NaOH this is 40.0.
- 0.9 g
- Exothermic. -327.9 kJ
- PV=nRT, where P = pressure, V = volume, n = number of moles, R = gas constant,
T = absolute temperature
- . 1.1 atm.
- . 2.4 atm.
- . 2.8 g/l
- . A polar compound has a distribution of charge over the molecule
which gives a separation between the center of positive charge and the center
of negative charge. A non-polar compound has a symmetrical distribution of
charge.
- . The temperature will drop steadily until it reaches 0 oC.
It will remain at this temperature for as long as it takes to freeze solid,
at which time the temperature of the ice will again decline until it reaches
the temperature of the surroundings.
- . If a system at equilibrium is disturbed, it will shift to minimize
the effect of the disturbance. For example if the following gaseous reaction
has come to equilibrium
H2 + I2 --> 2 HI
and more H2 is pumped in, more HI will be formed to use up some
of the H2 and restore the equilibrium.
- . Molarity (M) is defined as moles of solute per liter of solution.
M = 0.2
- .A saturated solution is a stable solution which contains as much of a solute
as can be dissolved at the particular temperature. A supersaturated solution
is in a metastable state, and is prepared by cooling a saturated solution
so that it now contains more solute than the equilibrium amount. Disturbing
the solution by scratching the container or adding a crystal will often cause
the excess to precipitate. Think of crystals slowly forming in honey, which
is a supersaturated sugar solution.
- . More oxygen dissolves as the pressure of oxygen above the water
increases. Henry's law can be used to calculate this change: X (aq)
= K Px where X (aq) is the concentration of dissolved gas
in the aqueous phase, Px is the partial pressure of gas above the water, and
K is the Henry's law constant for the particular gas.
- . Freezing point is lowered when salt is added.
- .
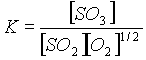
- . More SO3 will form.
- . 1.6 x 10-5 = [Pb+2][Cl-]2
, so Pb+2 = 1.6 x 10 -2 M
- . Addition of a common ion, one which appears in slightly soluble
salt, will repress the solubility of the salt. For instance, if some
sodium chloride is added to the system in Q. 21, the solubility of PbCl2
would be decreased.
- . Invoking the common ion effect: 1.6 x 10-5 = [Pb+2][Cl-]2
where Cl- is now 1 M. Pb+2 = 1.6 x 10-5.
- . A strong acid is completely ionized in solution, an weak one is
not.
- . pH = - log [H+] , pH = 3.7
- . [H+][OH-] = 1 x 10-14, pH
= 9.5
- . 5.0 x 10 -6
- . Acid base buffer is a solution which resists pH changes
from addition of either acid or base. It is composed of a weak acid and its
salt or a weak base and its salt.
- . The rate of a reaction depends on the concentrations of the reactants
and the temperature. A rate usually increases with temperture. The activation
energy is energy which must be supplied to begin a reaction, which may be
substantial even if the reaction is spontaneous. (e.g. Methane and air will
burn, but only if the reaction is started by a spark) A catalyst usually increases
the rate of a reaction, by lowering the required activation energy.
Return to problem set