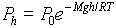 or
or 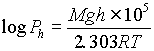
The Atmosphere
Atmospheric reactions
Energy balances in the atmosphere
Radiation transfers through atmosphere
Weather and climate
Physical characteristics of the atmosphere
Major components
Minor components
Trace gases
Pressure, Density, and Altitude
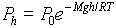 or
or 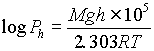
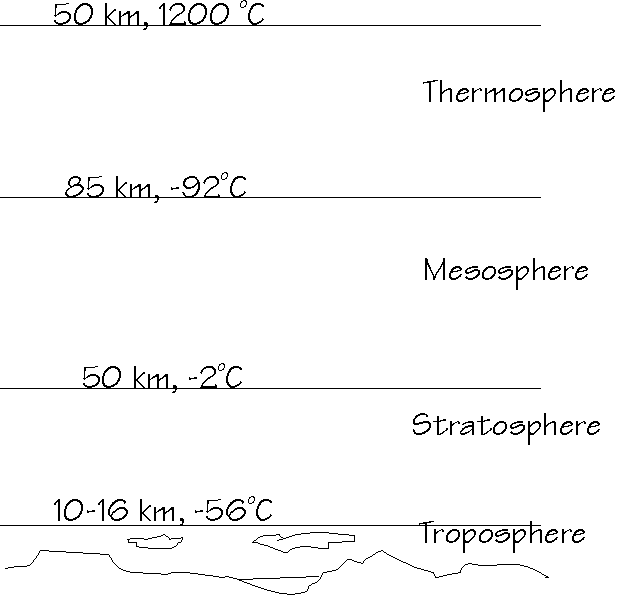
Temperature also varies with altitude
Stratification of the atmosphere
Energy transfers:
Insolation--the solar constant
1.34 kW / M2 = 19.2 Kcal/min/M2
Half reflected directly or indirectly
other half reaches surface and is absorbed
Heat transport mechanisms
Conduction
Convection
Sensible heat
Latent heat
Radiation
Water vapor and Carbon dioxide and the greenhouse effect
Albedo
Mass transfer in the Atmosphere
Effect of water
Movement of air masses and convective energy transport
Fronts, winds and air currents
Lapse rates
Effect of topography
Global air circulation
Fronts and storms
Inversions and air pollution
Monsoons
Ice ages
Urbanization effect on microclimate
City heat domes
Photochemical reactions in atmosphere
Excited molecules
Absorption of light photon produces excited species. Energy lost by:
| Physical quenching |
| Dissociation |
| Direct reaction |
| Luminescence, |
fluorescence, phosphorescence, chemiluminescence
| Intermolecular energy transport |
| Intramolecular energy transport |
| Spontaneous isomerization |
| Photoionization |
Free radicals in the atmosphere
Chain propagating and chain terminating reactions
Hydroxyl and hydroperoxyl radicals in the atmosphere
Evolution of the atmosphere
Acid base reactions in the atmosphere
Carbon dioxide
Sulfur dioxide
Basic particulates
Ammonia
Atmospheric Oxygen
Ozone
Nitrogen in atmosphere
Carbon dioxide
Water
Particles