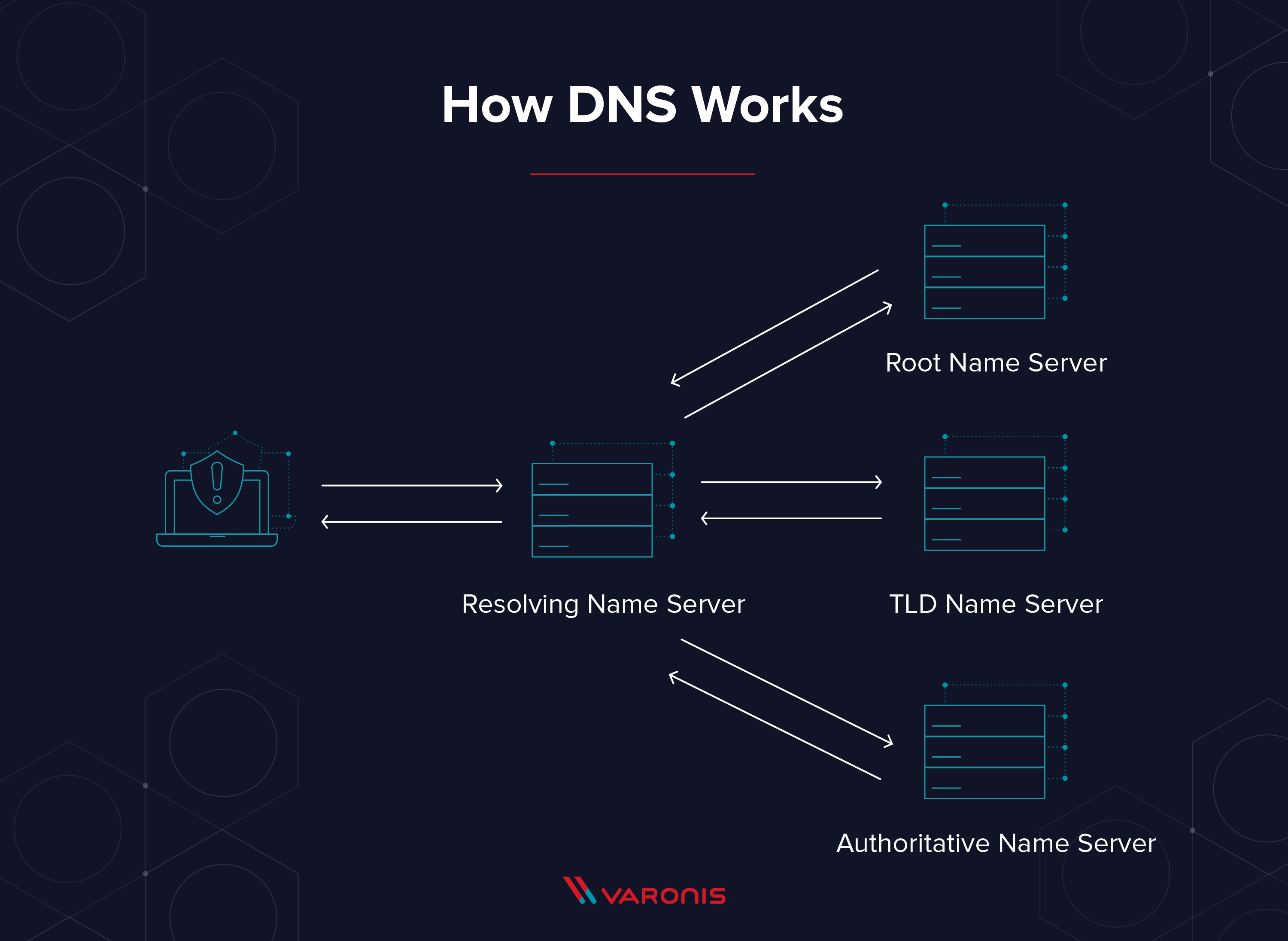
A system called the domain name system or DNS associates websites with the corresponding address and your computer uses the DNS to look up names and get the associated IP address which is used to connect your computer to the destination on the internet. There is no way one DNS can handle all the requests from all devices. The answer to this problem is DNS servers are connected in a distributed hierarchy and are divided into domains (.com, .net, and, .org.) DNS was originally created to be a public communication protocol for government and educational institutions because of this it was susceptible to attacks like DNS spoofing. That’s when a hacker taps into a DNS server and changes it to a domain name different from the IP addresses and directs you to another website.
