Blood system biology
Blood clot (a.k.a. thrombi) formation and their breakup (a.k.a. embolism) can potentially lead to life-threatening complications when occurring in the heart (i.e., a heart attack), brain (i.e., a stroke), or lungs (i.e., DVT/PE). Among these, thrombo-embolic infarction is the leading cause of mortality and morbidity in the United States, while stroke is the 5th.
Dr. Voronov’s group has done extensive work at the interface of cutting-edge live animal experiments, advanced biomedical imaging and supercomputer blood flow simulations.
Selected Publications:
- Is the Endothelial Cell Responsible for the Thrombus Core and Shell Architecture? O. E. Kadri, M. Surblyte, V. D. Chandran and R. S. Voronov. 2019, Journal of Medical Hypothesis, 129, 109244.
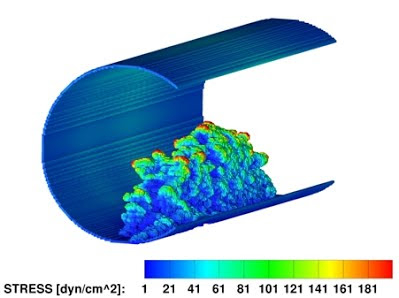
- In vivo measurement of blood clot mechanics from computational fluid dynamics based on intravital microscopy images. Kadri OE, Chandran VD, Surblyte M, Voronov RS. Comput Biol Med. 2019 Mar;106:1-11. doi: 10.1016/j.compbiomed.2019.01.001. Epub 2019 Jan 11.
- A systems approach to hemostasis: 1. The interdependence of thrombus architecture and agonist movements in the gaps between platelets
JD Welsh, TJ Stalker, R Voronov, RW Muthard, M Tomaiuolo, et al.
Blood, blood-2014-01-550335
- Simulation of intrathrombus fluid and solute transport using in vivo clot structures with single platelet resolution
RS Voronov, TJ Stalker, LF Brass, SL Diamond
Annals of biomedical engineering, 2013. 41 (6), 1297-1307
- Hierarchical organization in the hemostatic response and its relationship to the platelet signaling network
Timothy J Stalker, Elizabeth A Traxler, Jie Wu, Kenneth M Wannemacher, Samantha L Cermignano, Roman Voronov, Scott L Diamond, Lawrence F Brass. Blood, blood-2012-09-457739
